WHO ARE WE?
We make INNOVATIVE digital ecosystem servicing clients across green mobility. We have a long term experience dealing with regional governments, municipalities and private sector operators. To integrate digital solutions in ecosystems, we elevate SMART CITY to DIGITAL CITY SOULUTIONS.
MOBILITY
WHAT IS HYDROGEN?
Hydrogen is not a direct source of energy but rather an energy carrier. It serves primarily as a means of storing energy, especially for renewable energy when all their production can not be consumed. It can also be used to produce energy, to power hybrid vehicles or autonomous energy production systems. The heat produced during the hydrogen production process can also be used locally to heat buildings for example.
HOW IS HYDROGEN MADE?
- Reforming natural gas with superheated steam, which is a widely used process.
- In the gasification process, charcoal is burned in a reactor. At very high temperatures, the released gases reform to produce H2 and carbon monoxide.
- Separating water into oxygen and hydrogen with electrolysis. This process is interesting as it makes it possible to easily obtain a pure hydrogen, and most importantly, is the only one to be totally carbon-free if the electricity is provided through renewable sources such as wind & solar.
ADVANTAGES AND BENEFITS OF HYDROGEN
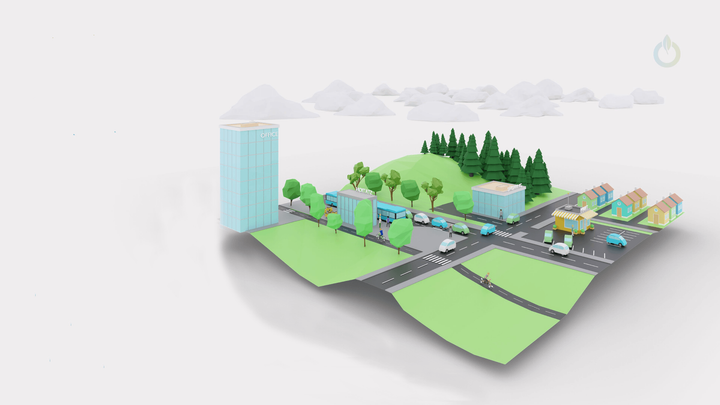
GREEN DIGITAL CITY ECOSYSTEM
INCREASED CITY FUNCIONALITY
Means a functioning city economy,employment opportunities, access to essential aspects of prosperity - to infrastructure services such as connectivity and connectivity; reliable, sustainable and low-cost energy sources; adequate educational opportunities; affordable forms of housing and efficient transport.
HIGHES LIVING STANDARDS
In a smart city, citizens have access to a comfortable, healthy, clean, safe and active lifestyle, which includes several aspects such as cheap energy, convenient public transport, quality education, faster public services, clean water and air, low crime rates, and access to a variety of entertainment and cultural opportunities.
SUSTAINABILITY
Providing citizens with access to the resources they need with a view to securing them for future generations. Sustainability is the method by which resources are not depleted or permanently destroyed. Sustainability is not only linked to the environment, but also to the economy.
BOOSTING LOCAL ECONOMY
Keep money in the local economy. Using local sourcens and include local citizens. They keep money within the local community that would otherwise flow out to external enviroment.
ECOSYSTEM
Intergration of Green mobility and Digital City Ecosystem in one complex interoperable digital platform